Ovarian Cancer

At our health care facility, we understand the importance of quality care when it comes to ovarian cancer. That’s why we trust Dr. Rani Bhat, the leading gynecological oncologist in this field for last 26 years, to offer the best treatment options for ovarian tumor management. With vast experience and knowledge of ovarian cancer symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment, Dr. Bhat will work with you to develop a personalized plan for your successful treatment.
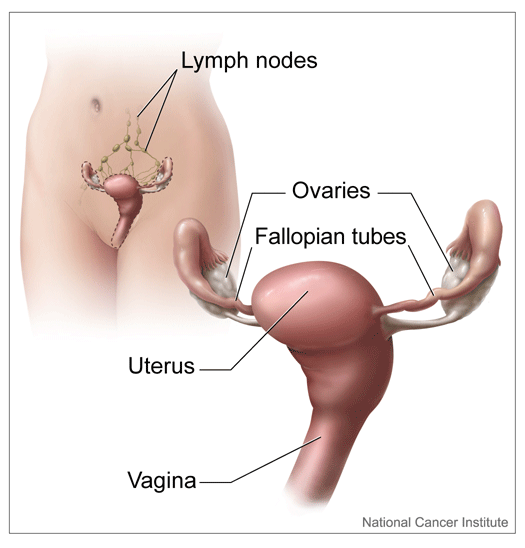
Where are the ovaries situated in the body?
What are the causes of ovarian cancer?
-
Risk increases with age.
-
Obesity or being overweight.
-
Risk is slightly higher in women who have not had children.
-
Risk is high in women who have had early menarche (first menstruation) and late menopause.
-
If there is a family history of ovarian or breast cancer (genetic BRCA1 and BRCA2). 1% of ovarian cancers may be due to hereditary.
-
Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome (HBOC): women with HBOC are characterized by a high risk of breast and ovarian cancers and they also tend to develop primary peritoneal cancer.
-
Hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome (HBOC): women with HBOC are characterized by a high risk of breast and ovarian cancers and they tend to develop cancer at an earlier age than the general population. The absolute lifetime risk of developing cancer with HBOC as compared to the general population.


Ovarian Cancer Symptoms?
-
Pain in the tummy
-
Abdominal swelling
-
Swollen abdomen
-
Feel lump in your tummy
-
Feeling full even with a small meal
-
Loss of appetite
-
Loss of weight
-
Frequency of passing urine
-
Constipation
-
Heartburn
-
Some ovarian tumours can also cause menstrual irregularities
-
In young women, ovarian tumours can cause hormonal changes such as excessive hair growth on the body, change in voice, and change in the external genitalia

What tests will be required for diagnosis?
-
To confirm the diagnosis
-
The doctor will usually do a vaginal examination (internal examination) if you have symptoms that may possibly be like cancer.
-
-
Assessing the extent and spread
-
Further tests may be advised to assess if cancer has spread to other organs such as an ultrasound scan, a CT scan, PET CT an MRI scan, a chest X-ray, blood tests like CA125 tumor marker, or other tests.
-
This assessment is called the staging of cancer, done to assess the extent of the spread and to know the stage.
-
If your tummy is swollen with fluid (called ascites) of mass, you may be advised to have this fluid drained or have a biopsy of the mass. This is usually done with the help of ultrasound (ultrasound guidance). The removed fluid or biopsy of the mass may be checked for cancer cells.
-

_b.png)
Ovarian Cancer Treatment
Surgery
-
Ovarian cancer treatment has to be perSurgery is the mainstay of treatment. The type of surgery will depend on the stage of cancer and the age of the patient.
-
The guideline is to remove womb with the cervix (total hysterectomy), both ovaries and fallopian tubes (bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy), fatty apron near the stomach (omentum) and fatty tissue (lymph glands) and to remove all the visible tumor, this surgery is known as cytoreductive surgery (CRS). There are various surgical treatments for ovarian cancer depending on the stage of cancer and other considerations. Aim of the surgery is – not gross tumor left behind.
-
HIPEC: hyperthermic intra-peritoneal chemotherapy is an intra-operative procedure which may be offered on a case to case basis. The principle of this procedure is that after complete removal of the tumor the tummy is washed with heated chemotherapy.

HIPEC

-
In young patients – fertility-sparing surgery can be offered in early stages, wherein only the effected ovary with cancer, omentectomy, and lymph glands are removed. Here the uterus and opposite ovary will be retained.
-
When the cancer is in advance stages, you may be advised to have neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NACT) to shrink the tumor and then go for CRS and then go for adjuvant chemotherapy, this is a kind of sandwich therapy: neo-adjuvant chemotherapy - CRS - adjuvant chemotherapy.

Chemotherapy:
-
In chemotherapy, treatment drugs are used to kill or slow the growth of cancerous cells. It’s usually given through an IV injection.

Follow-up after treatment?
-
You should strictly follow-up with your doctor as per their advice.
-
In addition to receiving treatment for cervical cancer, your success in treatment will depend only on when you have a regular follow-up.
Can we prevent ovarian cancer?
Though ovarian cancer is not preventable, women with the BRCA1 gene or a family history of this cancer should be monitored closely. Some women with genetic abnormalities choose to have prophylactic removal of the ovaries and fallopian tubes in order to prevent them from developing ovarian cancer.


-
There are two ovaries situated on either side of the uterus. Ovaries are oval in shape and are attached to the uterus with the help of a ligament called ovarian ligament.
-
The ovary has two main functions, one produces hormones and the other is it produces ovum every month. This ovum will be picked up by the fallopian tube and transferred to the uterus for fertilisation with the sperm.
-
Ovaries are situated in the lateral part of the pelvis called the ovarian fossa.

Dr. Rani Bhat is one of the best gynecologists in Bangalore. She completed her post-graduate training in Obstetrics and Gynecology (MS- Master of Surgery) and qualified for the prestigious fellowship of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists of UK (FRCOG).
She trained in the sub-specialty of Gynaecological Oncology by undertaking fellowships at the KK Women’s and Children’s Hospital and the National Cancer Centre - Singapore General Hospital. She also undertook a fellowship at the Queen Mary Hospital, the University of Hong Kong where she received further training in Gynaecologic Oncology and Robotic surgery. She received colposcopy training from Royal Women’s Hospital in Melbourne, Australia.
Dr. Bhat is Division Chief and Fellowship Director, Gynecologic Oncology at Apollo Hospital, Bangalore. She is a keen academician where she mentors young gynecologists' wishing to train in gynaecological oncology and has authored several chapters in textbooks of gynaecology and has published extensively on this subject in medical journals.
Her expertise lies in the treatment of cancers of the reproductive tract in women – ovarian, cervical, uterine (endometrial), vulvar and vaginal cancers. She is well known for her skills in advanced laparoscopic and robotic surgery, as well as ultra-radical surgery and HIPEC (Heated Intra-peritoneal chemotherapy). Dr. Bhat is also known for her surgical expertise in managing complex non-cancerous conditions such as severe endometriosis, adenomyosis, pelvic masses, ovarian cysts and fibroids.
Dr. Bhat’s approach to patient care is unique, she utilizes the latest and effective medical treatment combined with the old fashioned method of concern and respect for patients and their families. She is a strong proponent of evidence-based medicine and ensures that her patients understand their problem, the options available and are fully involved in planning treatment.
According to Dr. Bhat, the most gratifying part of her job is the opportunity to make a difference in the lives of women with cancer. She acknowledges that it gives her a great sense of purpose.
Education and Training :
Qualifications
-
MBBS
-
MS (Obstetrics & Gynaecology)
-
MRCOG (UK)
-
Diploma in Gynaecological Operative Endoscopy (France)

